Assembly statistics and evaluation¶
So, we now have an assembly of our reads in rna-assembly.fa. Let’s
take a look at this file –
head rna-assembly.fa
This is a FASTA file with complex (and not, on the face of it, very informative!) sequence headers, and a bunch of sequences. There are three things you might want to do with this assembly - check its quality, annotate it, and search it. Below we’re going to check its quality; other workshops do (will) cover annotation and search.
Applying transrate¶
transrate is a program for assessing RNAseq assemblies that will give you a bunch of assembly statistics, along with a few other outputs.
First, let’s download and install it:
cd
curl -O -L https://bintray.com/artifact/download/blahah/generic/transrate-1.0.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
tar xzf transrate-1.0.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
export PATH=~/transrate-1.0.2-linux-x86_64:$PATH
Now run transrate on the assembly to get some preliminary stats:
transrate --assembly=/mnt/work/rna-assembly.fa --output=/mnt/work/stats
This should give you output like this:
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n seqs 62
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : smallest 206
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : largest 4441
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n bases 81132
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : mean len 1308.58
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n under 200 0
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n over 1k 37
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n over 10k 0
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n with orf 41
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : mean orf percent 64.76
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n90 841
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n70 1563
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n50 1606
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n30 2070
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : n10 3417
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : gc 0.46
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : gc skew -0.04
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : at skew -0.05
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : cpg ratio 1.88
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : bases n 0
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : proportion n 0.0
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:38:11 : linguistic complexity 0.23
...which is pretty useful basic stats.
I’d suggest paying attention to:
- n seqs
- largest
- mean orf percent
and more or less ignoring the rest ;).
Note: don’t use n50 to characterize your transcriptome, as with transcripts you are not necessarily aiming for the longest contigs, and isoforms will mess up your statistics in any case.
Evaluating read mapping¶
You can also use transrate to assess read mapping; this will use read evidence to detect many kinds of errors.
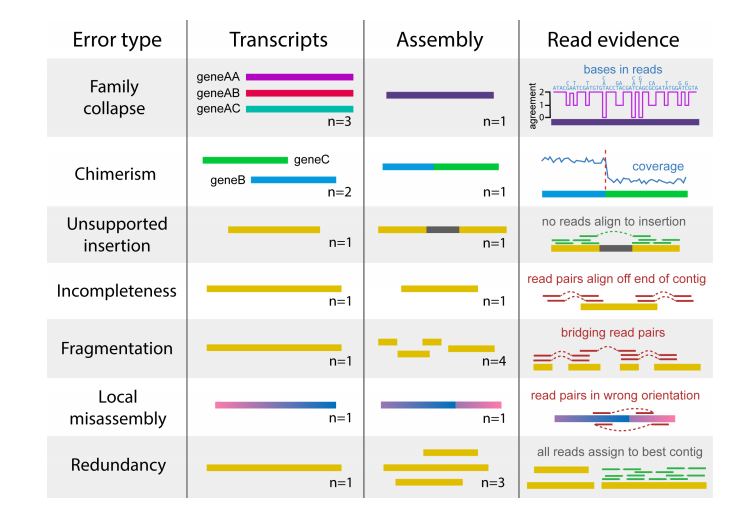
To do this, you have to supply transrate with the reads:
transrate --assembly=/mnt/work/rna-assembly.fa --left=/mnt/work/left.fq --right=/mnt/work/right.fq --output=/mnt/work/transrate_reads
The relevant output is here:
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : Read mapping metrics:
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : -----------------------------------
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : fragments 57178
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : fragments mapped 50925
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : p fragments mapped 0.89
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : good mappings 8297
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : p good mapping 0.15
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : bad mappings 42628
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : potential bridges 22
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : bases uncovered 11877
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : p bases uncovered 0.15
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : contigs uncovbase 48
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : p contigs uncovbase 0.77
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : contigs uncovered 13
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : p contigs uncovered 0.21
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : contigs lowcovered 25
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : p contigs lowcovered 0.4
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : contigs segmented 14
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : p contigs segmented 0.23
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : Read metrics done in 7 seconds
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:38:55 : No reference provided, skipping comparative diagnostics
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:43:11 : -----------------------------------
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:43:11 : TRANSRATE OPTIMAL SCORE 0.036
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:43:11 : TRANSRATE OPTIMAL CUTOFF 0.1589
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:43:11 : good contigs 27
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 13:43:11 : p good contigs 0.44
Using transrate to compare two transcriptomes¶
transrate can also compare an assembly to a “reference”. One nice thing about this is that you can compare two assemblies...
First, install the necessary software:
transrate --install-deps ref
Second, download a different assembly – this is done with the same starting reads, but without using digital normalization:
curl -O -L https://github.com/ngs-docs/2016-mar-nonmodel/raw/master/files/rna-assembly-nodn.fa.gz
gunzip rna-assembly-nodn.fa.gz
Compare in both directions:
transrate --assembly=/mnt/work/rna-assembly.fa --reference=/mnt/work/rna-assembly-nodn.fa --output=/mnt/work/assembly-compare1
and
transrate --reference=/mnt/work/rna-assembly.fa --assembly=/mnt/work/rna-assembly-nodn.fa --output=/mnt/work/assembly-compare2
In this case you can see that our assembly “covers” more of the other assembly than the other assembly does ours.
Merging two (or more) assemblies¶
Finally, you can also use transrate to merge contigs from multiple assemblies, if you’ve used read mapping –
transrate --assembly=/mnt/work/rna-assembly.fa \
--merge-assemblies=/mnt/work/rna-assembly-nodn.fa \
--left=/mnt/work/left.fq --right=/mnt/work/right.fq \
--output=/mnt/work/transrate-merge
and at the end you’ll see you have more “good” contigs –:
[ INFO] 2016-03-30 15:50:54 : p good contigs 0.52
Back to index: 2016 / Mar / mRNAseq on non-model organisms
LICENSE: This documentation and all textual/graphic site content is licensed under the Creative Commons - 0 License (CC0) -- fork @ github. Presentations (PPT/PDF) and PDFs are the property of their respective owners and are under the terms indicated within the presentation.